Preparation product
Your current position:Home > Preparation product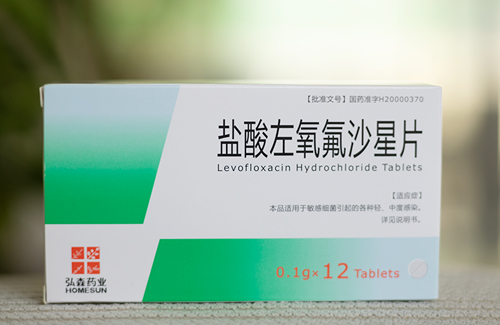
- Levofloxacin Hydrochloride
Levofloxacin Hydrochloride Tablets specification
Please use it under the guidance of the doctor
[drug name]
Generic name: Levofloxacin Hydrochloride Tablets
Hydrochloride Tablets Levofloxacin
Chinese Pinyin: Zuoyangfushaxing Pian Yansuan
[character] this product is a kind of white to light yellow film.
[indications]
This product is applicable to the following light and moderate infection caused by sensitive bacteria:
Respiratory system infection, acute bronchitis, acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis, diffuse panbronchiolitis, bronchiectasis with infection, pneumonia, tonsillitis (peritonsillar abscess);
Urinary tract infections: acute pyelonephritis, complicated urinary tract infection;
The reproductive system infection: acute prostatitis, acute epididymitis, intrauterine infection, uterine accessory is phlogistic, pelvic inflammatory disease (suspected with anaerobic infection can be combined with metronidazole).
Skin and soft tissue infection: infectious impetigo, cellulitis, lymphatic (node) inflammation, subcutaneous abscess, perianal abscess;
Intestinal infection: bacterial dysentery, infectious enteritis, Salmonella enteritidis, typhoid and paratyphoid;
Sepsis, granulocyte reduction, and various infections in patients with low immune function;
Other infections: mastitis, trauma, burn and postoperative wound infection, abdominal infection (and, if necessary, combined with metronidazole), cholecystitis, cholangitis, bone and joint infections and ENT infections.
[Specification] according to 0.1g calculation C18H20FN3O4
[usage and dosage]
Oral, adult 0.1g~0.2g (1~2 tablets) each time, two times a day. The condition of the disease can be increased to three times a day.
[adverse reactions]
This product is levofloxacin hydrochloride, the active ingredient of levofloxacin, the literature reported that the relevant circumstances are as follows:
1 serious and other important adverse reactions
Following serious and other important adverse reactions have been in [note matters in detail: tendinitis and tendon rupture, myasthenia gravis deterioration, hypersensitivity, other serious and sometimes fatal reactions, liver toxicity, central nervous system effects, Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea, peripheral neuropathy, prolongation of the QT interval, pediatric patients with musculoskeletal disorders, blood disorders, photosensitive / light toxicity and resistance in bacteria.
According to the report, the use of quinolones (including levofloxacin) may lead to crystallization urine, urinary tube. Therefore, for levofloxacin in the treatment of patients undergoing shall maintain proper hydration, to prevent the formation of highly concentrated urine.
2 clinical trial experience
Because the clinical trial is performed under different conditions and observed in clinical trials of a drug adverse reaction rate cannot be directly and other drugs in clinical trials in the adverse reaction rate compared to, and does not necessarily reflect the adverse reaction in the actual application rate.
Below is a description of the data, reflecting the 7537 patients, 29 phase III clinical trials of levofloxacin integrated exposure. The average age of the study population for 50 years old (about 74% of the population < 65), which 50% male, 71% were white, 17% were black.
Patients were treated with levofloxacin for a wide range of infectious diseases.
(see indication). Patients received a dose of levofloxacin for 750mg once a day, 250 mg once a day, or 500mg 1 or 2 times a day, usually 3~14 days of treatment, the average duration of treatment was 10 days.
The total incidence of adverse reaction, the type and distribution of levofloxacin in the use of 750 mg once a day, 250 mg once a day, or 500 mg daily for 1 or 2 times with similar. A total of 4.3% patients discontinued due to adverse drug reaction of levofloxacin, in 250 mg and 500 mg per day dose patients, the proportion was 3.8%; in an 750 mg daily dose in patients with adverse drug reactions this proportion was 5.4%. under 250 mg and 500 mg daily dose in patients with the most common cause of discontinuation of gastrointestinal reaction (1.4%), mainly for nausea and vomiting (0.6%), (0.4%). Dizziness, headache (0.3%) and (0.2%). In an 750 mg daily dose in patients with the most common adverse drug reactions lead to discontinuation of gastrointestinal reaction (1.2%), mainly for nausea and vomiting (0.6%) (0.5%), dizziness (0.3%) and headache (0.3%).
In the table below (Tables 1 and 2) were cited happen to is more than or equal to 1% of the acceptance of the adverse reaction of levofloxacin in the treatment of patients, and occur in 0.1 to < 1% accept the adverse reaction of levofloxacin in the treatment of the patients. The most common adverse reactions (more than or equal to 3%) were nausea, headache, diarrhea, insomnia, constipation, dizziness and.
Table 1: common report in Levofloxacin in clinical trials (more than 1%) adverse reaction
Note: N A. = 7274; N=3758 B. (female).
Table 2: adverse reactions (N=7537) reported in clinical trials of levofloxacin (1% to 0.1).
Note: N A. = 7274
In the use of multiple dosing in the treatment of clinical trials, noticed in the acceptance of quinolone antibiotics, including levofloxacin in the treatment of patients, ophthalmological abnormalities, including multiple punctate cataract and lens. Now there is not a drug and these events.
3 post market monitoring
The following table (Table 3) lists of levofloxacin was approved in the use of identification of adverse reactions. Due to these reactions is from the indefinite number of people spontaneously reported, and sometimes can not reliably evaluation the incidence of these events, or a drug exposure and the causal relationship between these events.
[taboo]
The quinolone allergy, pregnancy and breast-feeding women, disabled patients under the age of 18.
[note]
This product is levofloxacin hydrochloride, the active ingredient of levofloxacin, the literature reported that the relevant circumstances are as follows:
Tendinitis and tendon rupture in 1
Patients of all age groups, the use of fluoroquinolone antibiotics including levofloxacin, risk treatment in patients of tendinitis and tendon rupture occurred. The most common adverse reactions include Achilles and Achilles to the Achilles tendon, Achilles tendon repair surgery has been reported. The site of rupture occurred tendinitis and tendon including shoulder, hand muscle two head the thumb and other parts of the tendon.60 years, or at the same time the use of corticosteroids, or accept the risk of kidney, heart and lung transplant the occurrence of fluoroquinolone associated tendinitis and tendon rupture is further increased. In addition to age and glucocorticoid use, can lead to increased risk of tendon rupture factors include intense physical activity that has to have renal failure and rheumatoid arthritis. Tendon damage has been reported without the presence of risk factors in patients with the use of mefloquine Nobel Ketones by tendinitis and tendon rupture. After the end of the process of drug or medication can tendon rupture occurred, has been the end of the medication after a few months of tendon rupture reported. If a patient presents with pain, edema, inflammation or tendon rupture should disable levofloxacin, discovery have symptoms of muscle tendinitis and tendon rupture shall immediately advise patients to rest, and contact their health care provider to consider changing with non quinolone treatment.
2 myasthenia gravis worsening
Including levofloxacin, fluoroquinolone antibiotics will result in neuromuscular blocking, may exacerbate myasthenia gravis myasthenia gravis. Including death and the need for ventilatory support, listed after serious adverse events, and myasthenia gravis patients using fluoroquinolones related. To avoid the known history of myasthenia gravis patients with levofloxacin.
3 hypersensitivity reaction
The use of fluoroquinolones, including levofloxacin for the treatment of patients with occasional severe and sometimes fatal hypersensitivity and / or allergic reaction, the reaction occurred in the first time after treatment. Some reactions may be accompanied by cardiovascular collapse, hypotension / shock, seizures, loss of consciousness, tingling sense of angioedema (including the tongue, throat, pharynx or facial edema / swelling), airway obstruction (including bronchial spasm, shortness of breath and acute respiratory distress), dyspnea, urticaria, pruritus and other serious skin reactions. For the first time in a rash or hypersensitivity to any other symptoms should immediately stop using levofloxacin severe acute hypersensitivity to epinephrine treated at the same time, according to take other measures such as oxygen recovery, the clinical need of intravenous fluids, use of antihistamines, corticosteroids, l Amine drugs and treatment of airway pressure.
4 other serious and sometimes fatal adverse reactions
Use including levofloxacin, fluoroquinolone antibiotics treatment in patients with very few cases occur serious, and sometimes even life-threatening adverse reactions, some of these adverse reactions is hypersensitivity, some unknown etiology. These adverse reactions can very serious, usually occurs in many times after treatment. Clinical manifestations include one or more of the following:
Fever, rash, or severe skin reactions (e.g., toxic epidermal necrosis, loose solution, erythema, erythema);
Vasculitis; arthralgia; myalgia; serum sickness;
Allergic pneumonia;
Interstitial nephritis; acute renal failure or renal failure;
Hepatitis; jaundice; acute liver necrosis or liver failure;
Anemia, including hemolytic anemia and aplastic anemia, thrombocytopenia, including thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura; leukopenia; agranulocytosis; blood cells reduce disease and / or other blood diseases.
In the first rash or other symptoms of allergy symptoms should immediately stop using the drug and take appropriate support measures.
5 liver toxicity
Has received treated with levofloxacin in the treatment of the patients appeared severe liver toxicity, including acute hepatitis and lethal events after the report of the listed. In more than 7000 patients in clinical trials and found no evidence of severe drug-induced liver toxicity. Severe liver toxicity usually occurs within 14 days after the start of treatment, in most of the disease name, in the treatment was started within 6 days. Most severe liver toxicity in the name of the disease has nothing to do with the allergy. Most fatal liver toxicity report found in age is more than or equal to 65 patients, most and high-sensitivity independent. If patients with signs and symptoms of hepatitis, it shall immediately stop the use of levofloxacin.
6 central nervous system effects
There have been a fluoroquinolone antibiotic use including levofloxacin, patients with seizures and psychosis reported.
Quinolones can also lead to increased intracranial pressure and central nervous system symptoms, causing tremor, restlessness, anxiety, dizziness, confusion, hallucinations, delusions, depression, nightmares, insomnia, very few cases can lead to patients with Dutch act thoughts or actions. These reactions may occur in the first time after treatment. If the use of levofloxacin in patients experiencing these reactions should be discontinued immediately and take appropriate treatment measures. The same as other quinolone antibiotics, such as known or suspected patients with epilepsy prone or lowered seizure threshold (such as cerebral arteriosclerosis, severe epilepsy) CNS disease or other risk factors prone to epilepsy the seizure threshold (or reducing treatment, such as the use of certain drugs in patients with renal insufficiency) should be used with caution in levofloxacin.
7 Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea
According to the report, almost all antibiotics (including levofloxacin) may have caused by Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) and severity can be from mild diarrhea to fatal enteritis. Antibiotic treatment can alter colonic normal flora, Clostridium difficile blooms. Clostridium difficile can produce toxins A and B, and then promote the CDAD. Due to infection of the disease name antibacterial treatment of difficult to onset and may required colonic resection, producing toxin of Clostridium difficile strains can increase the morbidity and mortality of the disease. After the use of antibiotics for the diarrhea of all patients should be considered CDAD. reports of CDAD in the use of antibiotics
2 months later, it is necessary to have a close look at the history of the disease.
If you suspect or have the diagnosis of CDAD, you need to stop does not directly for the antimicrobial treatment of Clostridium difficile. According to the clinical needs suitable management of liquid and dielectric, supplementation of protein given against C.difficile treatment and evaluation of surgical treatment.
8 peripheral neuropathy
Including levofloxacin, fluoroquinolone antibiotics treatment for patients suffering from rare appeared sensory nerves or sensory motor axon of neuron disease, lesions can be involved small axons and / or large axons, cause paresthesia, dysesthesia, touch the pain and weakness. If the patient has neuron disease symptoms such as pain, burning sensation, tingling, numbness and / or weakness or other sensory disorder such as light touch, pain, temperature sensation, sense of position and vibration vision abnormal, should immediately stop the use of levofloxacin to avoid the development of irreversible damage.
9.QT interval prolongation
Including levofloxacin, some fluoroquinolone antibiotics can make the electrocardiographic QT interval prolonged, a few patients can appear arrhythmia. Postmarketing surveillance during spontaneous reports, including torsades de pointes ventricular tachycardia in patients with rare of levofloxacin, quinolone antibiotics in the treatment of the patients. Known to prolong the QT interval of the patients and the uncorrected hypokalemia patients and the use of class IA (quinidine, procainamide) and class III (amiodarone, cable sotalol) antiarrhythmic drugs should be avoided in patients with the use of levofloxacin. Elderly patients are more likely to cause the influence of drug associated QT interval.
Musculoskeletal disorders in 10 pediatric patients and the effect of joint disease in animals
In pediatric patients (equal to or more than 6 months), levofloxacin only for to anthrax inhalation (exposure) protection. And compared to the control, in the acceptance of levofloxacin in the pediatric patients was observed in musculoskeletal disorders (joint pain, arthritis, disorder of tendon and gait abnormal) incidence rate increased.
In juvenile rats and dogs, oral and intravenous given levofloxacin resulted in the increase of osteochondrosis. To receive levofloxacin without adult dogs weight-bearing joint pathological examination showed the presence of cartilage damage sustained by. Other quinolones can also be in multiple species not adult animals produced in the joint bearing similar erosion and joint disease other signs.
11 blood sugar disorder
And other fluoroquinolone antibiotics, has been about blood sugar disorder such as symptoms of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia were reported. This occurred in oral hypoglycemic agents (such as glyburide / glibenclamide) or use insulin to diabetic patients. Therefore, for such patients, it is recommended should closely monitor the change of the level of blood glucose. If patients receiving levofloxacin in the treatment of hypoglycemia reaction, should immediately stop using levofloxacin and take appropriate treatment measures.
12 photosensitive / photo toxicity
Use of fluoroquinolones may cause after exposure to sunlight or ultraviolet light to moderate severe light sensitivity / light toxicity, which may is exposed to light area (typically including facial, neck V, forearm extensor side, back of the hand) excessive sun reaction (for example sunburn, erythema, and exudation, blisters, bullous edema). Therefore, we should avoid excessive exposure to the light source.
In the event of a photosensitive / photo toxicity, the drug should be discontinued.
13 production of drug resistant bacteria
Prescribe and not prescribe levofloxacin in the case of not yet diagnosed or highly suspected bacterial infections and do not meet the indications for prevention.
To bring benefits to patients, and increase the risk of drug-resistant bacteria.
[pregnant and lactating women] did not carry out the test and no reliable references.
The trial was not carried out and there was no reliable references.
The trial was not carried out and no reliable references were made.
There is no reliable reference to the test and no reliable references.
[storage] light shading, sealed preservation.
[packing] plastic packaging, 6 tablets / plate / box, 10 / plate / box, 12 x 2 / plate plate / box, 12 / plate / box, 10 x 2 / box / plate plate.
[Effective] 36 months
[executive standard] < Chinese Pharmacopoeia >2015 edition two
[approval] Zhunzi H20000370




 苏公网安备 32058502010036号
苏公网安备 32058502010036号